This macro shows you how to access files and folders using CAA V5 portable automation objects.
It creates a text file, fills it with data, copies this file and re-extracts the data from the copy.
CAAInfFileAccess is launched in CATIA [1]. No open document is needed.
CAAInfFileAccess.CATScript is located in the CAAScdInfUseCases module. Execute macro (direct execution of the macro only works on windows).
CAAInfFileAccess includes five steps:
- Prolog
- Deleting Existing Files if Needed
- Creating the Input File
- Duplicating the Input File
- Extracting Data from the Output File
Prolog
...
Dim sLF as String
sLF = Chr(10)
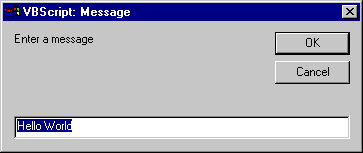
Dim sMessage as String
sMessage = InputBox ("Enter a message", "Message", "Hello World")
' ------------------------------------------
' Get the file system object
Dim oFileSys as FileSystem
Set oFileSys = CATIA.FileSystem
' ------------------------------------------
' Retrieve a folder for temporary files
Dim sTmpPath as String
sTmpPath=CATIA.SystemService.Environ("CATTemp")
If (Not oFileSys.FolderExists(sTmpPath)) Then
Err.Raise 9999,,"No Tmp Path Defined"
End If
...
|
A variable is defined for the LineFeed character. The InputBox function asks the user to enter a message string whose default value will be "Hello World".
The FileSystem object is the root object for all file/folder access. Input and output files will be created in the folder dedicated to temporary CATIA data. We use the SystemService object to get its full path defined in the CATTemp environment variable.
The existence of this folder is checked using the FolderExists
method of the FileSystem object.
Deleting Existing Files if Needed
...
' ------------------------------------------
' Delete possibly existing input and output files
Dim sFilOu As String ' Output file full path
sFilOu = sTmpPath & "/caatmpfilou.txt"
If (oFileSys.FileExists(sFilou)) Then
oFileSys.DeleteFile sFilOu
End If
...
|
FileExists and DeleteFile, two methods of the
FileSystem object are used to check the existence of the output
file and delete it if needed. The same operation is then performed on the
input file.
Creating the Input File
...
' ---------------------------------------
' Create file FilIn
Dim oFilIn As File
Set oFilIn = oFileSys.CreateFile(sFilIn, FALSE)
Dim oStream As TextStream
Set oStream = oFilIn.OpenAsTextStream("ForWriting")
oStream.Write "<MESSAGE>" & sLF
oStream.Write "<VALUE>"
oStream.Write sMessage
oStream.Write "</VALUE>" & sLF
oStream.Write "</MESSAGE>" & sLF
oStream.Close
...
|
sFilIn contains the full path of the input file. This file is created
using the CreateFile method of the FileSystem object
that returns a File
object. The OpenAsTextStream method allows to return a TextStream
object from the File object. The ForWriting option
specifies that the content of this file will be modified. This TextStream
object makes it possible to manipulate the file content as a stream of
text.
Successive uses of the Write method fill the input file.
In this case, the message is wrapped by XML-like tags. The sLF
variable is used to specify the end of a line. The text stream is then
closed using the Close method.
Duplicating the Input File
...
' ---------------------------------------
' Duplicate FilIn in FilOu
oFileSys.CopyFile sFilIn, sFilOu, FALSE
...
|
The CopyFile method of the FileSystem object
creates a copy of the input file. It uses its full name, contained in the sFilIn
variable and uses the content of the sFilOu variable as full
name of the copy.
Extracting Data from the Output File
...
' ---------------------------------------
' Get the result from the output file
Dim oFilOu As File
Set oFilOu = oFileSys.GetFile(sFilOu)
Set oStream = oFilOu.OpenAsTextStream("ForReading")
Dim sBuffer As String
sMessage = ""
sBuffer = oStream.ReadLine
Do Until oStream.AtEndOfStream
sMessage = sMessage & sBuffer
sBuffer = oStream.ReadLine
Loop
oStream.Close
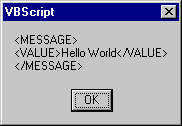
msgbox sMessage
|
Using the GetFile method, a File object is obtained for
the output file. OpenAsTextStream is then used to get a text
stream, but this time a ForReading usage is specified. The ReadLine
method is used in a loop to read each line of the output file. Each read
line is concatenated to the sMessage string. The end of the
file is detected using the AtEndOfStream method.
The sMessage variable now contains the whole content of
the output file. The MsgBox function is used to display this
content in a message box.